Octanol/water partition coefficient determination by VALLME
In most of the
applications, microextraction techniques are employed to isolate and/or enrich
target analytes from a given sample in order to make easier (more selective and
sensitive) their final determination by an appropriate instrumental technique. However,
the versatility of these techniques allows their use in the determination of
chemical constants. Researchers from the University of Alicante at Spain have
developed a vortex assisted liquid-liquid microextraction (VALLME) procedure to
determine the octanol-water partition coefficient (Kow) in a simple
way. Kow is an important parameter that can be used for different
purposes like the studies of the bioaccumulation rates of toxicants since Kow
is similar to the lipid-water partition coefficient or the proper selection of
an extractant in a extraction technique since Kow provides
information about the polarity of a compound.
In brief, the proposed
VALLME procedure consist on the addition of 50 µL of 1-octanol to 10 mL of an
aqueous solution of the compound under study. After a simple vortex assisted
agitation and centrifugation steps, a extract of 1-octanol with the target compound is obtained and analyzed by HPLC.
The
proposed method presents several advantages. The obtained values of Kow are
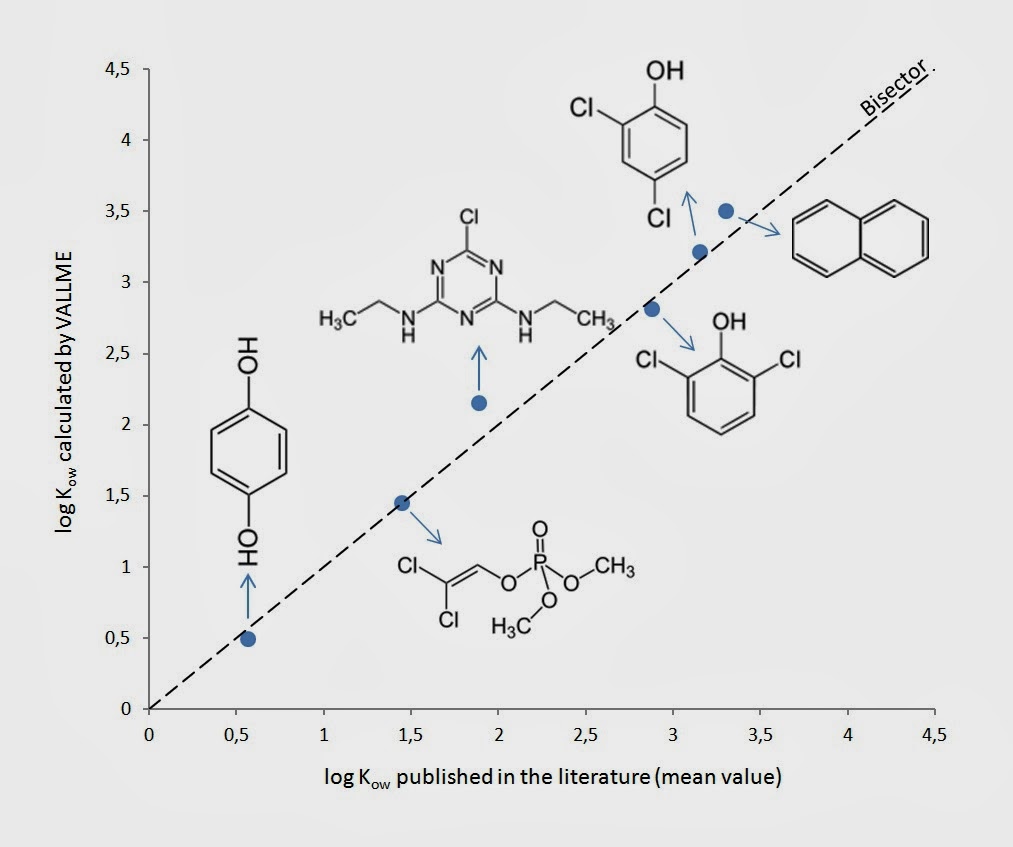
very good correlated with the reported values in the literature. This aspect is
clearly shown in the Figure where the Kow obtained by VALLME for six
different compounds (namely: hydroquinone; dichlorvos; simazine; 2,6 dichlorophenol; 2,4 dichlorophenol and naphthalene) are compared
with the reported values. The six compounds cover a wide range of polarities
which indicates the validity of the method. Moreover the method is faster than
its counterparts.
We strongly recommend this article to
our readers. In the original manuscript you will find interesting information
about the extraction time profiles of the different compounds, the comparison
with other accepted methods and the way to calculate the Kow.
Reference:
(1) Rapid determination of octanol–water partition coefficient using
vortex-assisted liquid–liquid
microextraction. Link
Comments
Post a Comment